
Tensorflow는 많은 기관, 학교, 기업에서 사용하고 있는 딥러닝 프레임워크입니다.
딥러닝을 학습하고 익히는데 있어 Tensorflow에서 제공하고 있는 튜터리얼을 살펴 보도록 하겠습니다.
다음은 텐서플로우 공식 튜터리얼 링크입니다.
url : https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/quickstart/beginner
바로 예제 코드부터 살펴보겠습니다.
"""
This Contents is about MNIST from Tensorflow Official Tutorial
url : https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/quickstart/beginner
All of the codes are from the url above.
"""
import tensorflow as tf # Import Tensorflow Library
# Load MNIST Dataset
MNIST = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = MNIST.load_data()
# Normalize the data
# MNIST is Image Data, so it is 0~255
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential(
[
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)), # Flatten the data
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation="relu"), # Dense Layer
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2), # Dropout Layer
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="softmax"), # Output Layer
]
)
# Compile the model
model.compile(optimizer="adam", loss="sparse_categorical_crossentropy", metrics=["accuracy"])
# Train the model
# epochs : How many times the model will be trained
model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5)
# Evaluate the model
# verbose : 0, 1, 2
# verbose mean how much information will be shown
model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=2)다음은 실행 결과입니다.
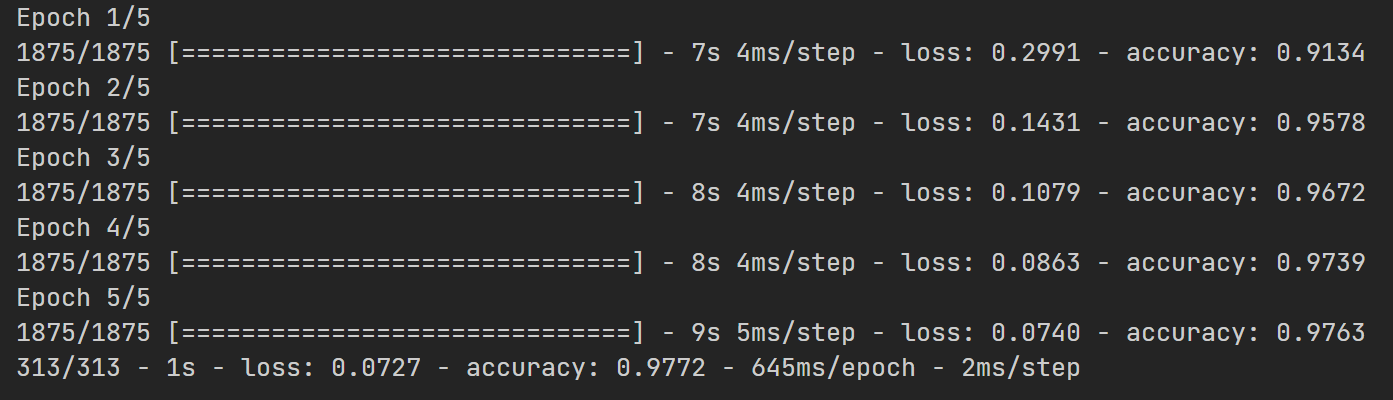
몇개의 레이어를 쓰지 않았지만 97프로라는 높은 결과값을 가지고 있습니다.
한번 살펴 보도록 하겠습니다.
import tensorflow as tf이 부분은 텐서플로우 모듈을 사용하겠다는 선언입니다.
그 다음은 데이터를 로드하는 것입니다.
# Load MNIST Dataset
MNIST = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = MNIST.load_data()
# Normalize the data
# MNIST is Image Data, so it is 0~255
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0- 여기서 MNIST라는 데이터를 불러옵니다. 데이터는 tf.keras.datasets에 있기 때문에 바로 불러올 수 있습니다.
- MNIST나 CIFAR 등의 데이터는 별도의 작업 없이 바로 불러올 수 있도록 되어있습니다.
- 많은 초보자들이 처음 접하는 데이터이기 때문입니다.
- MNIST데이터는 10개의 숫자로 이루어진 이미지입니다. 데이터는 GRAY 스케일로 이루어져 있고 0~255사이의 값을 가지기 때문에 /255.0을 통해서 0과 1사이의 값으로 바꾸어 줍니다.
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential(
[
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)), # Flatten the data
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation="relu"), # Dense Layer
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2), # Dropout Layer
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="softmax"), # Output Layer
]
)- 이 부분은 모델을 쌓는 부분입니다. 여기서는 한개의 Flatten과 2개의 Dense 1개의 Dropout을 사용하고 있습니다.
- Flatten은 2차원 데이터를 1차원으로 풀어헤치는 작접입니다. 28X28크기의 Image데이터를 한줄로 펼칩니다. 이는 Dense를 위한 사전 작업입니다.
- 펼처진 입력을 Dense (Fully Connected Layer)와 Relu 함수를 통해서 네트워크의 weight를 업데이트 해줍니다.
- 이후 Dropout 을 통해서 과적합을 방지해 줍니다. dropout은 랜덤하게 weight 값을 삭제합니다.
- 이후 10개의 레이블로 모으기 위해서 다시 한번 Dense 계층을 Softmax와 함께 거칩니다.
model.compile(optimizer="adam", loss="sparse_categorical_crossentropy", metrics=["accuracy"])- 이후 옵티마이저로 adam
- loss function으로 sparse_categorical_crossentropy로 모델을 설정해 줍니다.
# Train the model
# epochs : How many times the model will be trained
model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5)
# Evaluate the model
# verbose : 0, 1, 2
# verbose mean how much information will be shown
model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=2)- 이후 train과 evaluate를 통해서 모델을 학습하고 평가하게 됩니다.
- train은 포워딩과 백프로파게이션을 통해서 웨이트를 업데이트합니다. Tensorflow에서는 이러한 과정을 train함수로 추상화하여 제공하고 있습니다. 물론 직접 step을 설정하여 학습을 진행 할 수 있습니다.